魚眼カメラのキャリブレーション 〜 実装編1(ホモグラフィー行列と外部パラメータの計算)
ここでは,ホモグラフィー行列の計算と外部パラメータの計算を行っている下記の関数を見ていきます.(実装編0のコードにあった,Step2の CalibrateExtrinsicsが該当します.)
0.処理の流れ
具体的にやっていることとしては,キャリブボード上の点と画像に写っている点の対応関係からキャリブボードの回転・位置を計算します.この関数では,キャリブボードを撮影した一つ一つの写真が個別に処理されていきます.大きな処理の流れとしては,下記のようになっています.
1.ConvertVector2dToMat
ただのフォーマット変換なので,飛ばします.
2.ComputeExtrinsicsBasedOnHomography
ホモグラフィー行列を計算し,それを元に外部パラメータを計算します.多分全体のキモです.
該当部コード
下記,コードです.
void CalibrateExtrinsics(const vector<vector<cv::Point3f>>& objectPoints, const vector<vector<cv::Point2f>>& imagePoints, const IntrinsicParams& param, const int check_cond, const double thresh_cond, vector<cv::Vec3d>& board_rotations, vector<cv::Vec3d>& board_translations) { CHECK(objectPoints.size() == imagePoints.size()); CHECK(!objectPoints.empty() && !imagePoints.empty()); int image_num = imagePoints.size(); board_rotations.clear(); board_rotations.resize(image_num); board_translations.clear(); board_translations.resize(image_num); for (int image_idx = 0; image_idx < image_num; ++image_idx) { Mat board_rot, board_trans, jacobi_extrinsic; // Convert vector structure to cv:Mat structure. cv::Mat object_points_mat, image_points_mat; ConvertVector2dToMat(objectPoints[image_idx], imagePoints[image_idx], object_points_mat, image_points_mat); // Compute Extrisics Based on Homography. ComputeExtrinsicsBasedOnHomography(image_points_mat, object_points_mat, param, board_rot, board_trans); // Refine Extrinsics calculated in the above function. RefineExtrinsicsViaOptimization(image_points_mat, object_points_mat, board_rot, board_trans, jacobi_extrinsic, param, thresh_cond); // Check condition number for convergence. if (check_cond) { SVD svd(jacobi_extrinsic, SVD::NO_UV); if (svd.w.at<double>(0) / svd.w.at<double>((int)svd.w.total() - 1) > thresh_cond) { CV_Error(cv::Error::StsInternal, format("CALIB_CHECK_COND - Ill-conditioned " "matrix for input array %d", image_idx)); } } board_rot.copyTo(board_rotations[image_idx]); board_trans.copyTo(board_translations[image_idx]); } }
このエントリでは,ComputeExtrinsicsBasedOnHomographyを説明していきます.
1.ComputeExtrinsicsBasedOnHomographyの処理
おそらくキャリブレーション全体のロジックのキモになると思います.
1.TransformToNormalizedFrame
ホモグラフィー行列を実際に計算するにあたって,数値計算上の観点で正規化してます.ここも読んでいく中で初めて知ったんですが,点群位置の共分散をとって特異値分解することで正規化座標系をもとめることができるんですね.サラッと実装されてたんで調べるの大変でしたが...
2.ComputeHomography
ホモグラフィー行列を計算します.この関数内でも最適化計算をしてまして,,,ちょっと理解するのに時間がかかったんですが,ちょっとこのエントリに書くには大きいので,別のエントリを作ってリンクをここに持ってきます.
3.外部パラメータの計算部分
論文の主要部分です.
4.正規化した座標系からカメラ座標系への引き戻し
board_rot, board_transはカメラ座標系から見た書くキャリブボードの座標系でなければいけないので,座標を戻します.
該当部コード
void ComputeExtrinsicsBasedOnHomography(const Mat& image_points_mat, const Mat& object_points_mat, const IntrinsicParams& param, Mat& board_rot, Mat& board_trans) { CV_Assert(!object_points_mat.empty() && object_points_mat.type() == CV_64FC3); CV_Assert(!image_points_mat.empty() && image_points_mat.type() == CV_64FC2); // Transform points to the normalized coordinate on calibration board. Mat object_points_in_normalized_frame, rep_rot, rep_trans; TransformToNormalizedFrame( object_points_mat, object_points_in_normalized_frame, rep_rot, rep_trans); // Compute Homography. Mat H; { Mat imagePointsNormalized = NormalizePixels(image_points_mat, param).reshape(1).t(); H = ComputeHomography( imagePointsNormalized, object_points_in_normalized_frame( Rect(0, 0, object_points_in_normalized_frame.cols, 2))); // Norm of basis vector should be one. (r1, r2) double scale = .5 * (norm(H.col(0)) + norm(H.col(1))); H = H / scale; } // Axis and Rotation Matrix generation. cv::Mat rep_rot_in_cam; { cv::Mat u1, u2, u3; u1 = H.col(0) / norm(H.col(0)); u2 = H.col(1).clone() - u1.dot(H.col(1).clone()) * u1; u2 = u2 / norm(u2); u3 = u1.cross(u2); hconcat(u1, u2, rep_rot_in_cam); hconcat(rep_rot_in_cam, u3, rep_rot_in_cam); } // Compute calibration origin from representative origin. { cv::Mat rep_trans_in_cam = H.col(2).clone(); board_trans = rep_rot_in_cam * rep_rot.t() * (-rep_trans) + rep_trans_in_cam; cv::Mat board_rot_mat = rep_rot_in_cam * rep_rot.t(); Rodrigues(board_rot_mat, board_rot); } }
2.TransformToNormalizedFrameの処理
キャリブボード上の点座標を正規化しています.DLT法でホモグラフィー,基礎,基本行列を求める際のノウハウだと思うのですが,数値計算の誤差を抑えるために,点の重心を座標系の中心に持ってくるようにします.下記,点群座標の平均と共分散を求めて,共分散行列を特異値分解して回転行列を求めているんですが,このテクニックは知りませんでした.
該当部コード
void TransformToNormalizedFrame(const Mat& object_points_mat, Mat& normalized_object_points_mat, cv::Mat& rep_rot, cv::Mat& rep_trans) { // Compute COG and Angle via SVD. { Mat objectPoints = object_points_mat.reshape(1).t(); Mat objectPointsMean, covObjectPoints; calcCovarMatrix(objectPoints, covObjectPoints, objectPointsMean, COVAR_NORMAL | COVAR_COLS); SVD svd(covObjectPoints); rep_rot = svd.vt; if (norm(rep_rot(Rect(2, 0, 1, 2))) < 1e-6) { rep_rot = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64FC1); } if (determinant(rep_rot) < 0) { rep_rot = -rep_rot; } // rep_trans = rep_rot * objectPointsMean; rep_trans = objectPointsMean; int Np = objectPoints.cols; // Subtract translation from origin to normalize points. normalized_object_points_mat = rep_rot.t() * objectPoints + (rep_rot.t() * -rep_trans) * Mat::ones(1, Np, CV_64FC1); } }
3.ComputeHomography
Homography のトピックは大きいので,別のトピックに切り出しました.下記を参照あれ!
daily-tech.hatenablog.com
4.外部パラメータの計算部分
論文の主要部分ですが,キャリブボード上の点のZ座標が0であることを活かして,ホモグラフィー行列から外部パラメータを求めてます.u3 は u1 と u2 の外積から計算してます.
// Axis and Rotation Matrix generation. cv::Mat rep_rot_in_cam; { cv::Mat u1, u2, u3; u1 = H.col(0) / norm(H.col(0)); u2 = H.col(1).clone() - u1.dot(H.col(1).clone()) * u1; u2 = u2 / norm(u2); u3 = u1.cross(u2); hconcat(u1, u2, rep_rot_in_cam); hconcat(rep_rot_in_cam, u3, rep_rot_in_cam); }
5.正規化した座標系からカメラ座標系への引き戻し
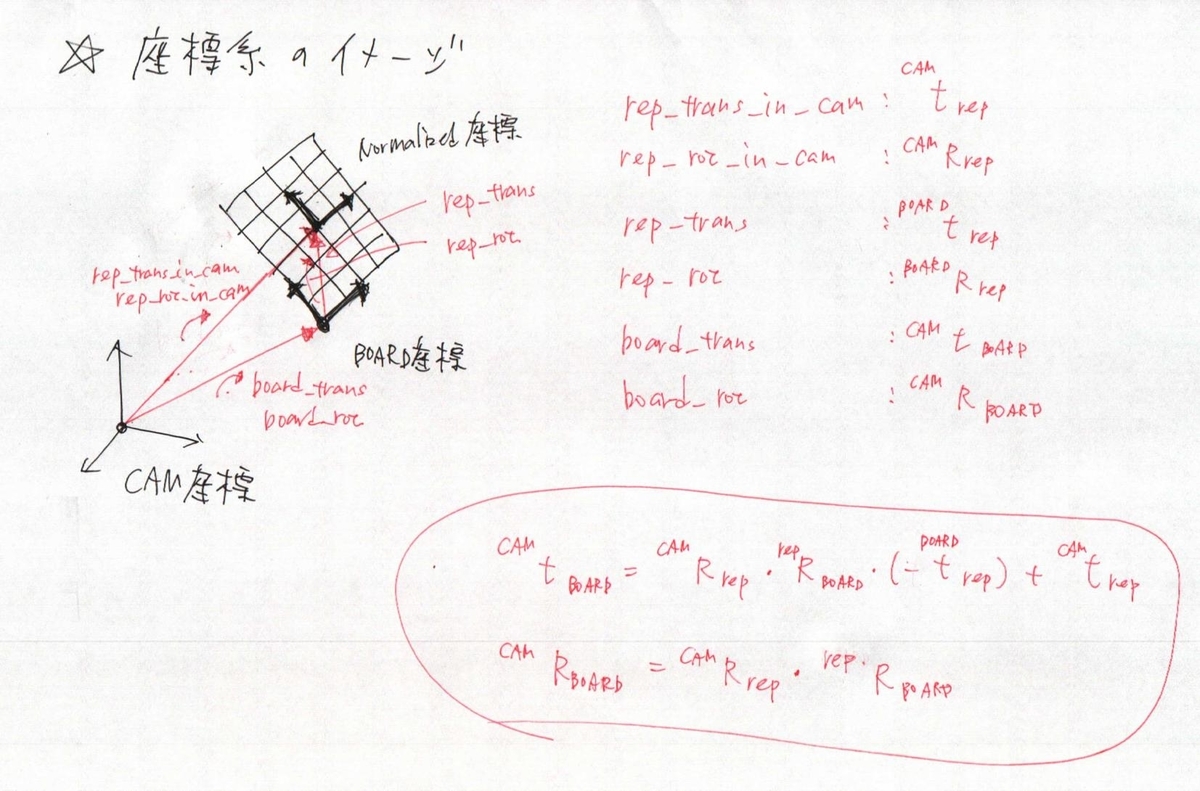
数値計算上都合のいい座標系から,カメラ座標系から見た座標系に戻してあげます.参考までに座標系のイメージを書いておきます.ホモグラフィーの計算とか重要なことはすべて正規化座標で実施して,最後に引き戻してます.
// Compute calibration origin from representative origin. { cv::Mat rep_trans_in_cam = H.col(2).clone(); board_trans = rep_rot_in_cam * rep_rot.t() * (-rep_trans) + rep_trans_in_cam; cv::Mat board_rot_mat = rep_rot_in_cam * rep_rot.t(); Rodrigues(board_rot_mat, board_rot); }
ということで,次は最適化の部分です!なんだか,思っていたよりとっても読みにくいエントリになってしまいました...魚眼のキャリブで困った人がいた時の助けになれば...
リファクタしたコードは下記のGithubにあげておきます.もちろん本家はOpenCVなので,あくまでも流れをつかむ用途でしか使えないですが...
github.com